The Hidden Cost of Aggregate in Load Support Applications
From laying the foundation for roadways to structuring parking lots and laydown yards, aggregate has been the backbone of construction projects around the globe. However, its omnipresence shouldn't overshadow the considerable expenses associated with its use, which stem from direct procurement, application costs, and other hidden factors.
Aggregate plays a crucial role in load support applications and infrastructure development, including roadways, parking lots, laydown yards, and other surfaces that must withstand significant weight and traffic. When constructing these surfaces, aggregate materials are commonly used to create a sturdy, supportive foundation known as the base course.
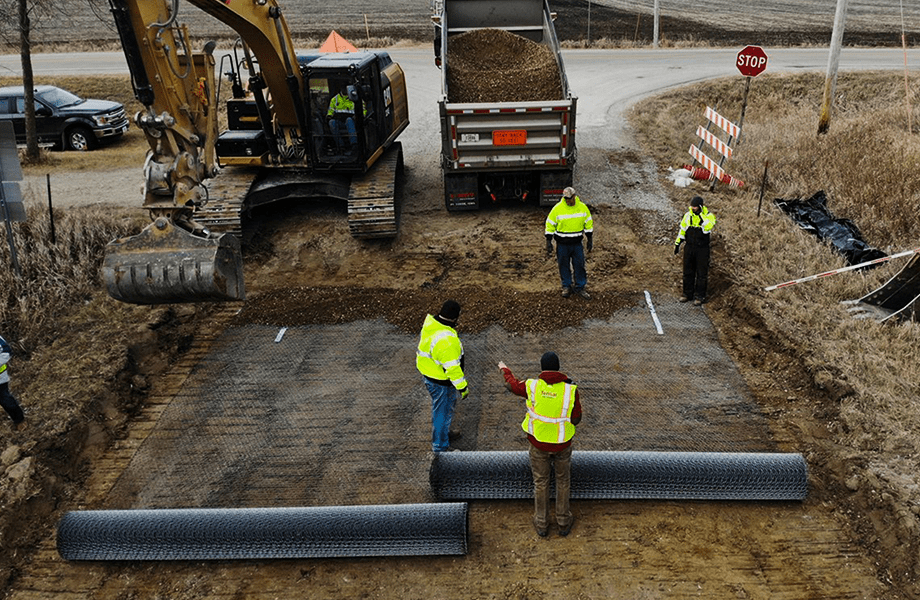
Load support applications in construction refer to any scenario where weight is to be transferred from an object (structure, vehicle, person, etc.) to the ground. Various methodologies and systems distribute loads or forces from a weighted object, ensuring stability, safety, and longevity. These applications are critical in virtually all aspects of construction, from buildings and bridges to roadways and retaining walls.
The purpose of load support systems is to ensure that the ground beneath a structure can adequately support the loads imposed on it throughout the structure's lifespan without undergoing unacceptable deformation, settlement, or failure. The characteristics of the site's soil or rock, the type and magnitude of the loads, and the nature of the structure itself (e.g., its size, weight, and use) all play a role in determining the appropriate load support system.

Aggregates are essential in various load support applications in the construction industry due to their high strength, stability, and drainage capabilities. Two of their key uses are in foundations and roadways. In foundations, they serve as backfill material, providing a sturdy base that evenly distributes the load to the soil below. The aggregate layer helps reduce the bearing pressure applied to the soil by spreading the load over a larger area, thus improving the performance and longevity of the foundation.
Aggregates are a fundamental component of the road base, subbase, and surface layers in road and pavement construction. The aggregate layers distribute the traffic load to the underlying subgrade, minimizing deformation and rutting. This is usually accomplished using crushed stone or gravel aggregates, known for their high strength and effective interlocking characteristics. These aggregates provide the necessary structural integrity for the pavement and enhance the road's overall durability and lifespan. They are also frequently used in embankment construction or fill sections, providing a stable base that distributes the load and prevents excessive settlement or deformation.

In every application, the choice of aggregate, including size, shape, and material properties, hinges on the specific project requirements. Their appropriate use is vital for achieving the desired performance and durability of the load support application.
Here are a few commonly used types of aggregate:
Crushed Stone: This versatile material is used in various applications, from road and bridge construction to buildings and landscaping. It provides excellent load-bearing properties and is available in a variety of sizes. Flexible base (flex base), also known as road base, is an important type of aggregate used in roadway construction. It provides a stable foundation for the pavement structure and helps distribute loads. Flex base is typically composed of crushed stone, gravel, or recycled materials and is designed to withstand the stresses and traffic loads experienced on roads and highways.
Gravel: Often used in constructing roads and driveways, gravel is a cost-effective option for many projects. It also allows for good water drainage, making it a good choice for wet areas.
Sand: While not used alone for load-bearing purposes, sand is often mixed with other aggregate types to fill gaps and add stability.
Recycled/Crushed Concrete: An eco-friendly alternative, recycled concrete can be crushed and used as an aggregate. It's gaining popularity due to environmental concerns and the availability of quality recycled concrete.
Slag Aggregates: Slag aggregates are obtained as a byproduct of iron and steel manufacturing. They have excellent strength and durability properties and are often used in road construction, concrete production, and railway ballast.
Ballast: Ballast is a specific type of coarse aggregate used in railway tracks and railroad construction. It provides stability, drainage, and support to the tracks, ensuring proper alignment and resistance against lateral movement.
Understanding the types and roles of aggregate in load support applications is critical to choose the correct material and managing its cost implications effectively.
1. Recycled Concrete Aggregate (RCA):
Recycled concrete aggregate is produced from waste concrete from demolition and renovation projects. It is processed and sized similarly to rock aggregate and can be used in the same applications, including roadways, parking lots, and laydown yards. RCA offers an environmentally-friendly and often cost-effective alternative, reducing the demand for virgin aggregate and the amount of construction waste that goes to landfills.
2. Recycled Asphalt Pavement (RAP):
RAP is the reclaimed and reprocessed pavement material containing asphalt and aggregates. RAP is often used to construct roadways and parking lots, providing a cost-effective and sustainable solution that reduces the need for virgin aggregate and new asphalt.
3. Expanded Shale, Clay, and Slate Lightweight Aggregate (ESCS):
This manufactured aggregate can be used as a lightweight replacement for natural aggregate. ESCS is made by heating clay, shale, or slate to high temperatures in a rotary kiln, which makes the material expand and become porous. It's lightweight and offers better thermal insulation and fire resistance.
4. Geosynthetics:
Geosynthetics, specifically geogrids, geotextiles, and geocells, offer effective solutions for enhancing the strength and stability of load-support applications while minimizing aggregate usage. Among these geosynthetic technologies, geogrids stand out with their demonstrated performance in interlocking with the aggregate, resulting in a stronger stronger, mechanically stabilized and more stable layer. Utilizing geogrids makes it possible to reduce the required depth of aggregate, thereby reducing the overall quantity of aggregate needed. This approach offers a compelling value proposition supported by decades of research on its performance. data on its performance. It is important to note that geotextiles and geocells also provide valuable contributions to load-support applications, each with its specific advantages and applications. The choice of geosynthetic depends on project requirements and engineering considerations.

Item 247 Flexible Base is a commonly specified aggregate in transportation agencies' specifications, including those of the Texas Department of Transportation (TxDOT). It is extensively used as a base material in roadway construction because it provides stable support and effectively distributes loads. The popularity of flex base 247 in Texas is evident from its frequent inclusion and quantities installed in public works construction projects recorded in TxDOT's database. It's noteworthy that aggregate preferences may vary in different regions, agencies, or organizations. Factors such as local geology, transportation infrastructure requirements, environmental considerations, and cost-effectiveness can influence the choice of aggregate materials.
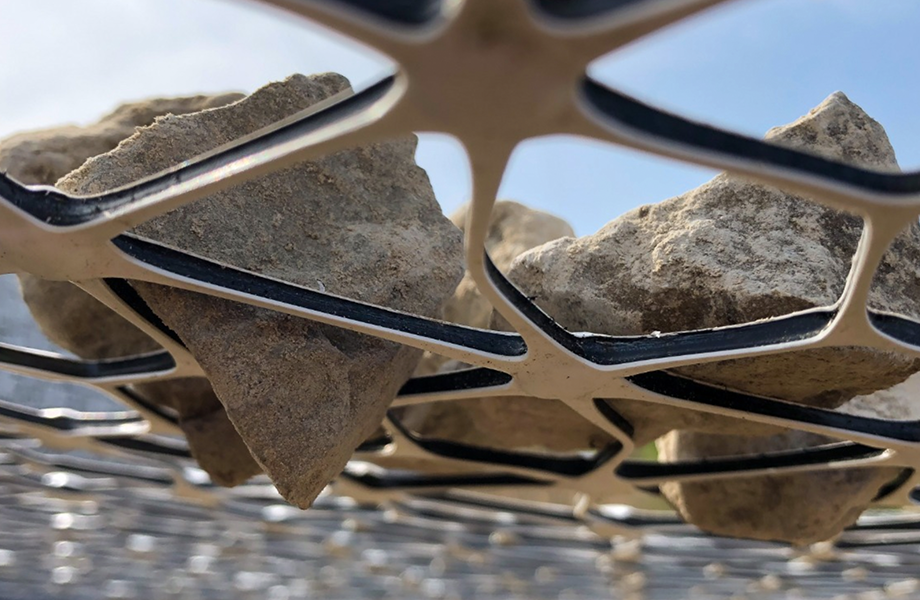

Tensar's InterAx geogrid offers a game-changing solution for mechanically stabilizing aggregates like Item 247 Flexible Base commonly used in road construction and other applications. By leveraging the benefits of InterAx geogrid, construction projects can achieve significant improvements in time and cost efficiency.
One of the key advantages of InterAx geogrid is its ability to distribute loads across a wider area, thereby minimizing the impact on the aggregate layer. This load distribution capability results in a reduced thickness requirement for the aggregate, leading to substantial material savings. The cost-effectiveness is particularly noteworthy considering the decreased transportation needs associated with using less aggregate.
Beyond material savings, InterAx geogrid enhances the structural integrity of roads by mitigating deformations like rutting, ultimately extending the lifespan of the pavement. This translates into long-term cost savings by reducing future maintenance and repair requirements. Furthermore, the installation process for InterAx Geogrid is relatively straightforward, allowing for efficient construction practices, reduced labor costs, and faster project completion.
LEARN MORE
In light of the growing demand for infrastructure development, the significance of aggregate in load support applications within the construction industry cannot be overstated.
However, with the rising costs associated with these materials, finding ways to reduce aggregate usage without compromising structural integrity is imperative. By carefully examining the role of Tensar InterAx Geogrid in Item 247 Flexible Base, it becomes evident that its implementation can significantly reduce the reliance on aggregate, resulting in substantial cost savings, improved time efficiency, and a reduced environmental footprint.
Embracing technological advancements and innovative materials like InterAx Geogrid presents a viable pathway forward, effectively addressing both the economic and environmental challenges inherent in modern construction while ensuring the long-lasting stability of our built structures.
Harness the power of Tensar InterAx Geogrid by greatly enhancing load-bearing capacity to support your ambitious projects while significantly reducing material and labor costs.
GET STARTED